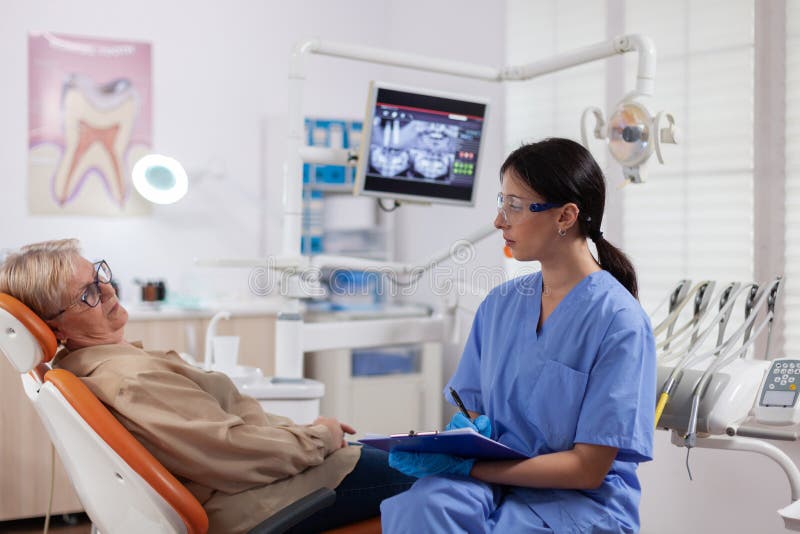
Contents
Common Oral and Dental Problems in Elderly
With advancing age, our mouth goes through a lot of chewing, grinding, gnashing and undergo a lot of wear and tear along with medical conditions and medications that can cause various oral and dental problems in the elderly!
As we get older, our bodies undergo different challenges and problems. Problems such as aging teeth and gums can increase the risk of various diseases while affecting overall oral health. Problems such as cancer, arthritis, and diabetes are some significant causes linked to oral health.
Unfortunately, many elderly cannot maintain good oral health either because of the lack of coverage or do not want to visit a dentist. Moreover, many adults lack dental insurance because they do not get any benefits once they retire. There is the federal Medicare program, though, but it doesn’t include routine dental care.
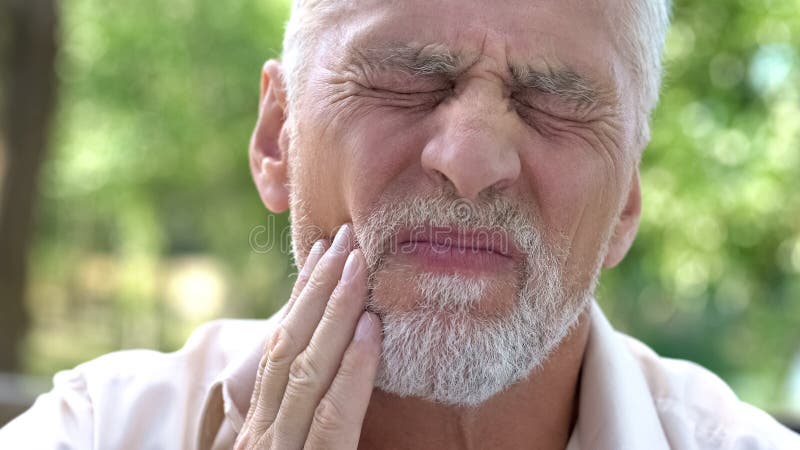
The mouth is like a window to your overall health. Taking care of yourself means being attentive about your physical capabilities and nutritional intake, and your tooth and gums. Common oral and dental problems in elderly people, such as periodontal disease, dry mouth, etc., impact overall health.
Poor oral health can worsen and cause severe issues such as diabetes, pneumonia or stroke, and heart disease. Moreover, oral pain can cause extreme uncomforting when eating or chewing, which can affect your nutrition.
Below, I will discuss common oral and dental problems in the elderly, their symptoms, and what preventive measures you can practice to prevent these issues.
Quick Points
- The use of mouthwash ad oral moisturizers help improve mouth health.
- Do not wait until you are thirsty. Drink water and carry a water bottle with you to make sure you constantly supply lubrication to your mouth.
- Stimulate saliva production by using lozenges and sugar-free gum.
- Avoid beverages that are harmful to your mouth. It includes carbonated soft drinks, coffee, alcohol, etc.
- Visit a physician regularly to consult whether to dosage or medication.
Common Oral and Dental Problems in Elderly
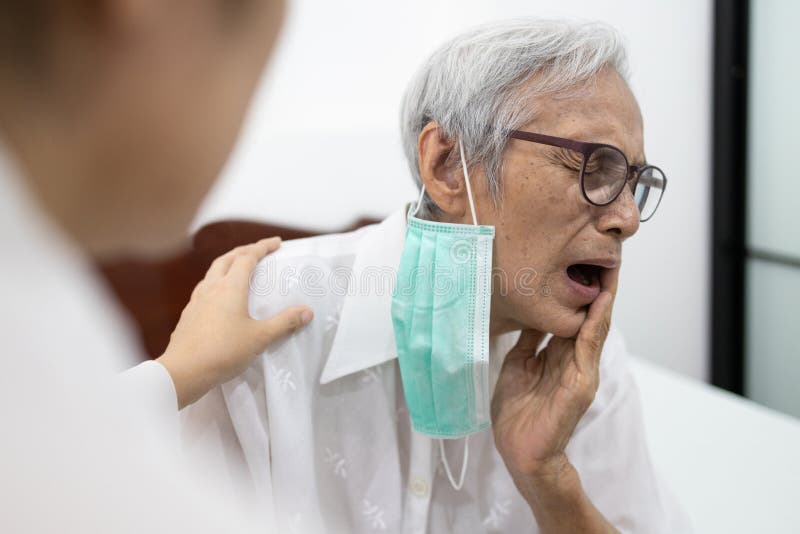

1. Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
Gum disease is one of the common oral and dental problems in elderly people. It is a gum infection that affects the soft tissues and may damage the bone supporting your teeth. The condition significantly contributes to loosening or tooth loss.
It is a common but preventable condition. The common cause of developing gum disease is poor oral hygiene. Getting regular checkups, brushing your teeth twice a day, and flossing daily can improve the condition and decrease the chances of developing it.
Symptoms
Snuggly-fitted, firm, and pale-pink gums are a sign of their excellent health. Symptoms of gum disease include:
- Tenderness when touched.
- Bleeding gums.
- Blood spitting when brushing.
- Purplish, dusky, or bright red gums.
- Puffy or swollen gums.
- Presence of pus between gums and teeth.
- Loss of teeth.
- Development of spaces between the teeth.
- Pain when chewing or grinding.
Causes
Gum disease generally starts with the plaque and the advancement of plaque called periodontitis. Some common causes of developing gum disease include:
The interaction of sugars in the food with bacteria in your mouth causes plaque. Although you can remove the plaque by brushing your teeth or flossing, it re-forms instantly. Moreover, tartar and plaque can cause more damage if they stay on your teeth for long periods. The best way to get rid of plaque and tartar to prevent developing gum disease is to get dental cleaning from your dentist.
Prevention
You can prevent developing periodontitis by developing rich oral hygiene that you can practice daily throughout your life. Good oral hygiene means flossing and brushing your teeth twice a day. Flossing before you brush also help you to remove bacteria and loosened food particles. However, if you take certain medications, smoke, or have a dry mouth, you should get a professional cleaning.
2. Tooth Cavities (Tooth Decay)
Tooth cavities or tooth decay is another common oral and dental problem in elderly people. In this case, a hole forms in the tooth. The condition begins with small cavities and gradually becomes wider if left untreated. Since they do not usually cause pain, it may be challenging to realize the problem. That is why a regular visit to your dentist can help detect tooth cavities.
Just because you think you have good oral hygiene doesn’t mean you cannot have a cavity. However, if your dentist found a cavity, some ways can treat it effectively.
Symptoms
Tooth cavities symptoms vary depending on the severity of the condition. It may include:
- White or black stains on your teeth.
- Tooth pain.
- Sensitive teeth.
- Holes in your teeth.
Causes
Plaque is the biggest culprit that significantly contributes to causing tooth cavities. In addition, it is a combination of acid, salvia, bacteria, and food particles. Moreover, since we have bacteria in our mouth, it turns sugar into acid when we eat or drink something that contains sugar. Plaque starts forming on your teeth, and the acid in it slowly erodes tooth enamel.
Tooth enamel means a hard protective coating that acts as a shield to prevent decay. As it weakens, the risk of developing tooth cavities increases. Almost all of us are at risk for cavities, regardless of how good our oral hygiene is. However, people with eating disorders, lack of fluoride, acid reflux, and dry mouth have more chances to develop tooth cavities.
Prevention
Since it is a common oral and dental problem in elderly people, the risk can be reduced by practicing the following:
- Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth twice a day.
- Eating and drinking less sugary food and drinks. It includes sweets, carbonated soft drinks, juices, candies, etc.
- Getting dental sealants on the teeth.
Moreover, eating foods that fight tooth decay, such as calcium-rich foods, black or green tea without sugar, fruits, and vegetables rich with fiber, and fluoride water, can help prevent the problem.
3. Canker Sore (Aphthous Ulcer)
Canker sores are tiny shallow lesions that occur at the base of the gums or on the soft tissues in the mouth. It is a common oral and dental problem in elderly people who lack zinc, vitamin B-12, or iron. The condition is pretty painful, and it can be hard for you to talk and eat.
However, in most conditions, they disappear on their own in a week or less. But, if you are suffering from painful canker sores that are large and don’t seem to heal, you should consult with your dentist.
Symptoms
Usually, they are white or yellow in an oval shape with a red border. They occur under the tongue or inside your mouth. You may suffer from a burning sensation or tingling a few days before they appear. There are various types of canker sores.
Minor Cankers Sores: They are the most common and heal on their own without scarring.
Major Cankers Sores: Unlike minor cankers, they are more extensive and profound, making them pretty painful. They also need more time to heal and may leave scarring.
Herpetiform Canker Sores: The rarest type of canker sores are herpetiform cankers that generally develop with advancing age. They are pinpoint in size, have irregular edges, and heal on their own without treatment.
Causes
There’s no apparent cause of canker sores. However, researchers suggest that there is more than one factor contributing to the cause of the problem. Possible causes of developing canker sores include:
- Mouth injuries caused by any dental work.
- Sports mishaps and overzealous brushing.
- The use of toothpaste that has sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Food sensitivities.
- The lack of vitamin B-12, zinc, and iron.
- Hormonal shifts linked to menstruation.
Prevention
Although canker sores disappear on their own, you can practice the following tips to reduce their frequency:
- Maintain a healthy diet plan. Try to avoid consuming foods that irritate your mouth. These may include certain spices, chocolate, chips, nuts, acidic fruits, etc.
- Good oral hygiene can also help prevent the problem. Make sure to brush your teeth after meals to keep them clean and free of food particles. Also, make that the brush you are using is soft.
- Stress is another reason that can cause canker sores. If this is the case, the use of stress-reduction methods, including meditation, can also be helpful.
4. Oral Cancers
Oral cancer occurs in the throat or mouth and damages the tissues. It is linked to a group of cancers known as head and neck cancers. Nowadays, it is among the most common oral and dental problems in elderly people. It develops in the cells (squamous) found in the lips, tongue, and mouth.
According to research, In the United States, over 49,000 cases of oral cancers are reported each year in adults over 40 years of age. Sometimes it is undiscoverable until it starts affecting the lymph nodes of the neck. If detected in the early stages, the chance of survival increases. Some common oral cancers include gums, lips, tongue, hard and soft palate, and floor of the mouth.
Symptoms
Some common oral cancer symptoms include:
- Loose teeth.
- Bleeding from the mouth.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Lumps in the neck.
- Earache that won’t heal.
- Numbness in the neck, face, or chin.
- Sore throat.
- Tongue pain.
- Jaw stiffness or pain.
Causes
One of the significant contributors to developing oral cancer is tobacco use, including chewing and smoking tobacco. Moreover, people who consume excessive alcohol are also high at risk of developing oral cancer. Other significant causes include:
- Poor nutrition.
- Previous diagnosis of the disease.
- A Weakened immune system.
- Genetic syndromes.
- A family history of any cancer.
- Chronic facial sun exposure.
- Being male.
Prevention
Maintaining good nutrition is an essential part to prevent oral cancer. Various treatments make it hard to eat or swallow. So, it is essential to consult your diet plan with your physician. Moreover, consulting with a nutritionist can also help plan a food menu that is gentle for your throat and mouth and that provides vitamins, calories, and minerals it needs. Keep your mouth moist and your teeth clean by drinking a lot of water and regular brushing.
If the problem is already there and in its early stages, surgery will be required to take the tumor and cancerous lymph nodes out. Other treatments to treat oral cancer include radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy.
5. Black Teeth
Black teeth are yet another common oral and dental problem in elderly people. Also, the condition may be a symptom of an underlying dental disease that you must not ignore. Teeth can be white, white-yellowish, or white-gray. If your teeth are white, it means there is enough calcium is present in the enamel.
In addition, the presence of calcium determines the color of your teeth. However, you may have a set of other materials in your teeth, making your teeth turn gray or yellow. Since the enamel starts thinning over time, it can cause an underlying layer called dentin to show through to make your teeth appear black.
Moreover, two common reasons turn your teeth black, which include:
Extrinsic: The damage caused by extrinsic appears outside your teeth. It includes tartar, staining, and other damages that damage the outer enamel.
Intrinsic: The damage occurs on the inside and progressively comes outward. It occurs when you are suffering from decay or any other damage due to a condition.
Symptoms
- Gray or brown spots on your teeth.
- Black, pinpoint-like areas below the gum line.
- Holes in the damaged enamel areas.
Causes
Several conditions can cause black teeth. They may include:
- The buildup of tartar and plaque on the teeth.
- The consumption of dark-colored food products, including cola and tea.
- Certain medications, such as liquid iron supplements.
- The use of tobacco.
Prevention
It is not possible to treat black teeth through home-based care. Instead, you should consult with a dentist. In addition, they will examine to determine the root cause before recommending you a treatment. Moreover, if your teeth turn black because of the tartar, the dentist will use special tools, such as hand scalers, to remove the tartar. Moreover, in some cases, a dentist may use a vibrating instrument (ultrasonic instruments) to break the tartar apart.
6. Uneven Jaw
Another common oral and dental problem in elderly people is the uneven jaw. It can make eating, talking, and breathing hard for a person. There are more than one causes that contribute cause uneven jaw. In some cases, the condition improves through physical therapy, while others require corrective surgery.
Symptoms
The uneven jaw has similar symptoms to those of other conditions, including:
- Clicking jaw.
- Temple pain.
- Popping in the ears.
- Tight jaw.
- Pain and swallow in the communal area of the jaw.
- Back or shoulder pain.
Causes
The health and functionality of tendons, muscles, and bones are essential for jaws. Imbalance in any of these parts can lead to uneven jaws. Various other causes can construct uneven jaws.
Broken Jaw or Trauma: Trauma can occur due to a fall or an accident, resulting in a fractured, broken, or dislocated jaw. A minor injury doesn’t require any treatment as it heals on its own. However, if your jaw is dislocated, it may need surgery.
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: They are common can cause by arthritis or trauma.
Birth Defects: Some people are born with an uneven jaw. The condition is also called “Faulty Jaw.” In this case, surgery along with supportive care and an improved lifestyle can help treat the problem.
Treatment
Most of the time, an uneven jaw requires surgery. However, the type of surgery your physician will suggest depends on the root cause. They may choose:
- Maxillary osteotomy surgery helps to correct open or bites. In that case, teeth and upper jaws moved forward to align them with lower ones.
- Genioplasty is helpful in the correction of the crooked chin. It helps to restructure the jaw and chin by cutting the chin bone.
- Mandibular Osteotomy handles issues related to protruding of the lower jaw or overbite.
Suppose your jaws are causing extreme pain, whether because of an injury or chronic condition, you should immediately consult with your doctor. They will detect the root cause to eradicate the problem.
Wrapping Up
Do not let preventable oral and dental problems in the elderly affect your overall health. In addition, taking preventive measures, such as keeping your mouth clean, developing and maintaining healthy oral hygiene, and regularly visiting your dentist, can help improve your overall health so you can always maintain a healthy smile.
Read More: