My Dad dealt with foot problems most of his life. But as he aged, I needed to find help for his new causes of foot pain in elderly feet. I researched many reputable sites and found some basic information. We eventually found a good podiatrist. He provided some great solutions for my Dad.
Contents
Most Common Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly People: A Comprehensive Overview
Foot pain is a common issue faced by elderly people, and it can significantly impact their daily activities and overall quality of life. With aging, the feet undergo various changes, making them more susceptible to pain and discomfort. Understanding the common causes of foot pain in the elderly can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment when needed. This article aims to explore some of the most common causes of foot pain in elderly adults.
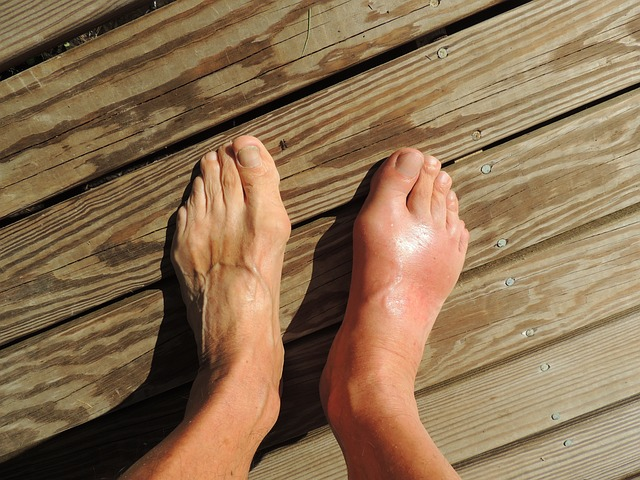
Normal Aging Changes
One major cause of foot pain in elderly individuals is the natural wear and tear of the feet over time, which can result in conditions like arthritis. Arthritis often occurs in the foot joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and a decreased range of motion. Additionally, poorly fitted or unsupportive footwear can exacerbate the foot problem further, causing further discomfort and even deformities like bunions and hammertoes. Another aspect to consider is that underlying health issues, such as diabetes and peripheral artery disease, can contribute to foot pain in the elderly. These conditions can affect blood flow and nerve function in the feet, leading to a range of symptoms like tingling, numbness, and increased sensitivity.
By being aware of these common causes of foot pain, elderly individuals can take steps to alleviate their discomfort and maintain their mobility. Often, simple changes such as new footwear make a big difference.
Causes of Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly Loved Ones
Arthritis
Arthritis is a common cause of foot pain in elderly people, as it affects the joints and can lead to inflammation and stiffness. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by reduced bone density, can increase the risk of arthritis, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the ankle joint. With age, the cartilage in joints may wear down, resulting in painful bone-to-bone contact and reduced mobility Mayo Clinic.
The most common type of arthritis in the elderly is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a condition that causes the cartilage in the joints to break down. This often leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints.
Arthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the feet. Foot arthritis cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and difficulty walking. It can also lead to other foot problems, such as bunions, hammertoes, and plantar fasciitis.
Additionally, pain from arthritis or other conditions often leads to decreased mobility. And when our elderly loved ones move less, it creates other aging issues. They need to stay as active as possible to help prevent falls, too.
There is no cure for arthritis, but there are treatments that can help to relieve the symptoms.
Treatment for Foot Arthritis May Include:
- Medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain relievers
- Physical therapy
- Exercise
- Weight loss
- Surgery
Often, simply choosing better fitting footwear helps alleviate some of the pain symptoms. Consider asking the doctor for help in choosing the best solutions.
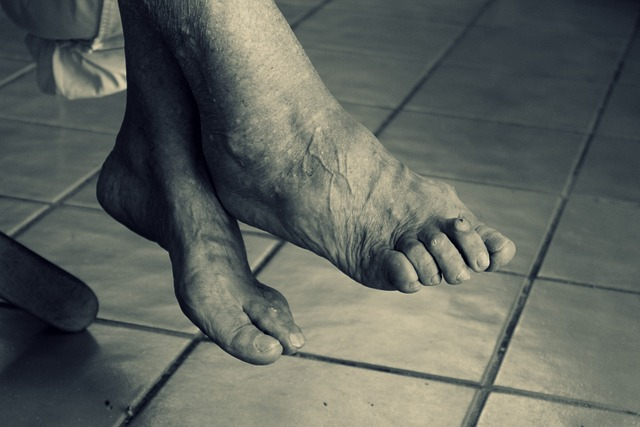
Bunions
Bunions are a frequent issue for elderly individuals, often causing pain, swelling and discomfort at the base of the big toe. They develop as a result of improper foot structure, arthritis, or wearing ill-fitting shoes. Obesity can also contribute to the development of bunions, as excess weight increases pressure on the foot Foot and Ankle Blog.
Bunions are a common foot deformity that can affect people of all ages, but they are more common in women and in the elderly. Bunions are caused by a misalignment of the bones in the big toe joint. This can cause the big toe to turn inward and the joint to become swollen and painful.
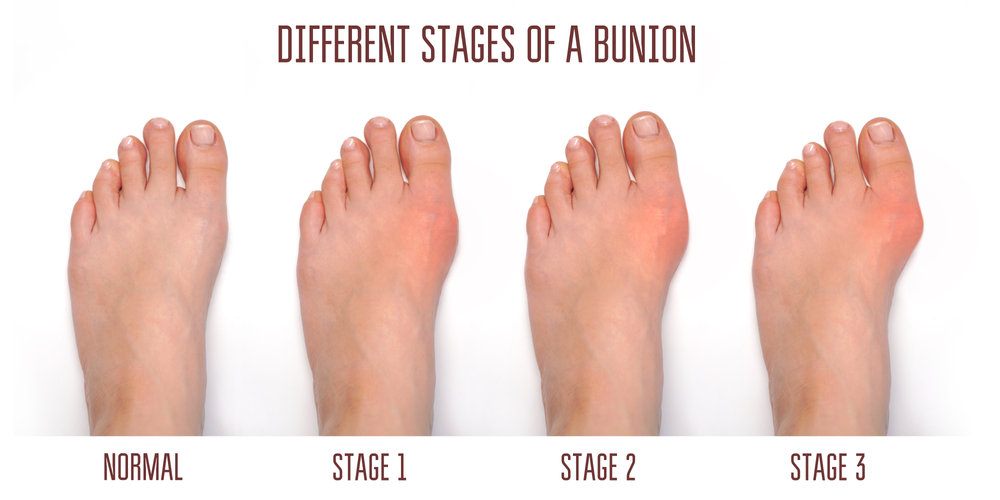
There Are a Number of Factors That Can Contribute to the Development of Bunions, Including:
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop bunions than others due to their genes.
- Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too narrow or that have high heels can increase the risk of developing bunions.
- Occupational factors: People who stand or walk for long periods of time are more likely to develop bunions.
- Arthritis: Arthritis can also increase the risk of developing bunions.
Bunions Can Cause a Number of Problems, Including:
- Pain: Bunions can be very painful, especially when walking or wearing shoes.
- Swelling: The joint around the big toe can become swollen and inflamed.
- Deformity: The big toe can become misaligned and turn inward.
- Ingrown toenails: The nail on the big toe can become ingrown, which can be very painful.
There Are a Number of Treatments for Bunions, Including:
- Shoes: Wearing shoes that are wide and have good arch support can help to relieve pain and pressure on the big toe joint.
- Orthotics: Orthotics are devices that can be placed in shoes to help correct the alignment of the big toe joint.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain relievers can help to relieve pain.
- Injections: Cortisone injections can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases of bunions. Surgery can correct the alignment of the big toe joint and relieve pain.
If your loved one experiences pain or discomfort in her feet, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent the condition from getting worse and helps maintain quality of life.

Hammertoes
Hammertoes occur when the middle joint of a toe bends abnormally, causing the toe to curl downward. This condition is often linked to muscle imbalances resulting from age, arthritis, or wearing tight shoes. Hammertoes can lead to painful corns and calluses and may impact mobility if left untreated Johns Hopkins Medicine. While Hammertoes are a common foot deformity that can affect people of all ages, they are more common in women and in the elderly. Hammertoes are caused by a bend in just the middle joint part of the toe. This can cause the toe to become stiff and painful.
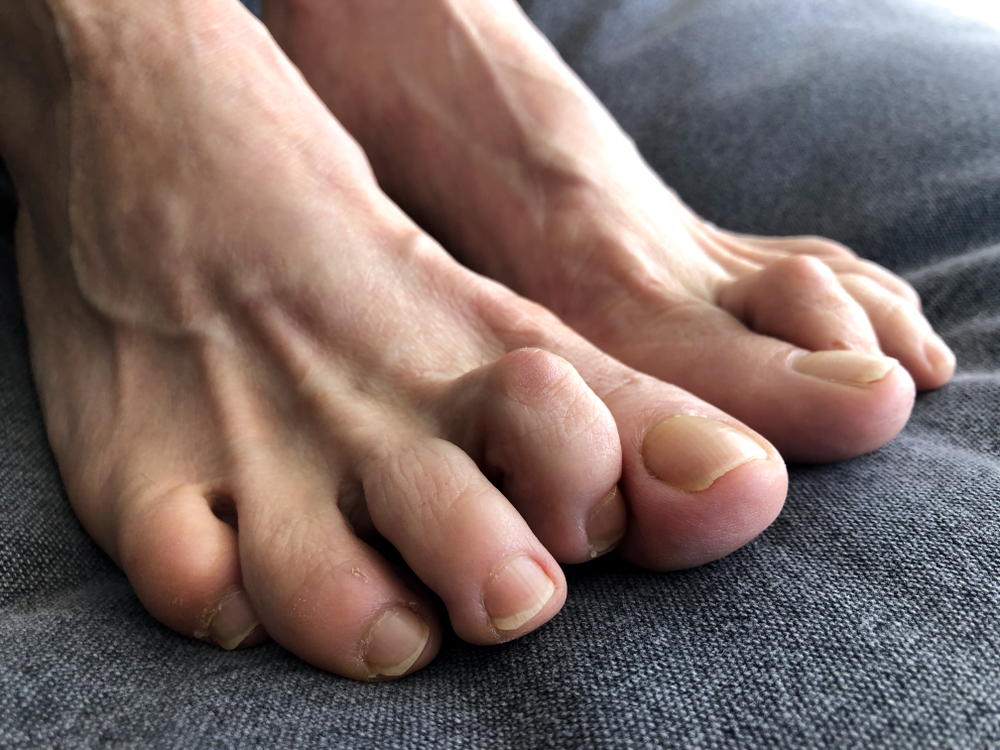
Hammertoes
There Are a Number of Factors That Can Contribute to the Development of Hammertoes, Including:
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop hammertoes than others due to their genes.
- Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too narrow or that have high heels can increase the risk of developing hammertoes.
- Occupational factors: People who stand or walk for long periods of time are more likely to develop hammertoes.
- Arthritis: Arthritis can also increase the risk of developing hammertoes.
Hammertoes Can Cause a Number of Problems, Including:
- Pain: Hammertoes can be very painful, especially when walking or wearing shoes.
- Swelling: The joint around the toe can become swollen and inflamed.
- Deformity: The toe can become misaligned and bent.
- Calluses and corns: The toe can develop calluses and corns due to pressure and rubbing.
There Are a Number of Treatments for Hammertoes, Including:
- Shoes: Wearing shoes that are wide and have good arch support can help to relieve pain and pressure on the toe.
- Orthotics: Orthotics are devices that can be placed in shoes to help correct the alignment of the toe.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain relievers can help to relieve pain.
- Injections: Cortisone injections can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases of hammertoes. Surgery can correct the alignment of the toe and relieve pain.
If your loved one experiences pain or discomfort in her feet, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment helps to prevent the condition from getting worse and helps to maintain quality of life.
Flat Feet
As people age, the natural arches in their feet may weaken and flatten. Flat feet can lead to foot pain, particularly in the heel and arch area, as the lack of support and cushioning puts added strain on the foot. Obesity and diabetes can exacerbate the issue, as both conditions may cause additional stress on the feet Verywell Health.
Also known as pes planus, flat feet often causes a number of problems, including pain, fatigue, and difficulty walking.
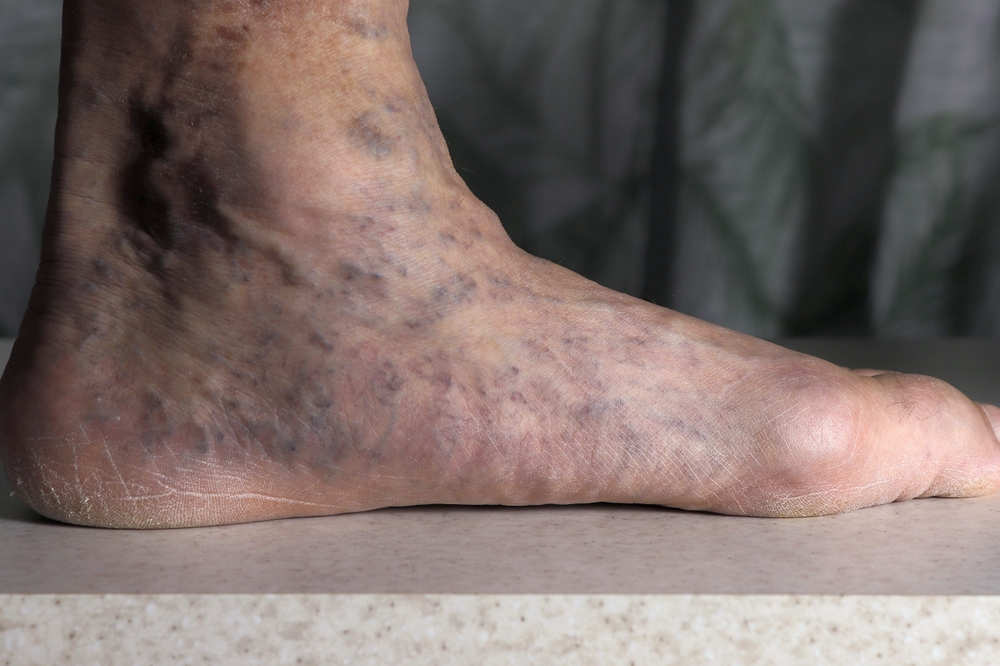
Flat Feet
Flat Feet Are More Common in the Elderly Due to a Number of Factors, Including:
- Age-related changes in the bones and muscles of the feet: As people age, the bones and muscles of the feet can weaken, which can lead to flat feet.
- Weight gain: Weight gain can put additional stress on the feet, which can lead to flat feet.
- Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, can increase the risk of developing flat feet.
If You Have Flat Feet, There Are a Number of Things You Can Do to Manage the Condition, Including:
- Wearing supportive shoes: Shoes with good arch support can help to reduce pain and improve walking.
- Exercise: Exercise can help to strengthen the muscles of the feet, which can help to support the arches.
- Losing weight: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help to reduce the stress on your feet.
- Seeing a doctor: If you are experiencing pain or other problems with your feet, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment.
By following these tips, you can help to your functional ability, manage flat feet and keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
Here Are Some Additional Information About Flat Feet:
- Symptoms: The most common symptom of flat feet is pain in the feet, especially after standing or walking for long periods of time. Other symptoms may include fatigue, difficulty walking, and swelling in the feet.
- Causes: The exact cause of flat feet is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, age, and weight.
- Treatment: There is no cure for flat feet, but there are treatments that can help to relieve symptoms. Treatment may include wearing supportive shoes, exercising, losing weight, and using orthotics.
- Prevention: There is no way to prevent flat feet, but there are things you can do to reduce your risk, such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly.
Bone Spurs
Bone spurs are bony growths that may form on the edges of bones, often as a response to joint damage from arthritis or other conditions. They can cause pain and discomfort by impinging on nearby soft tissue or nerves. In elderly individuals, bone spurs are commonly found in the foot and ankle area, which may lead to decreased mobility and balance issues WebMD. Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, are small, bony growths that can form on the joints. They are most common in elderly people, and they can affect any joint in the body, including the feet.
Bone Spurs Are Caused by a Number of Factors, Including:
- Degenerative joint disease: This is the most common cause of bone spurs. It is a condition that causes the cartilage in the joints to break down.
- Injury: An injury to a joint can also lead to the formation of bone spurs.
- Certain medical conditions: Bone spurs are more common in people with certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes.
Bone Spurs Themselves Are Usually Not Painful. However, They Can Sometimes Cause Pain and Other Problems, Such As:
- Pain: Bone spurs can press on nerves and other tissues, which can cause pain.
- Stiffness: Bone spurs can make it difficult to move the joint.
- Inflammation: Bone spurs can cause inflammation, which can lead to redness, swelling, and heat.
- Deformity: Bone spurs can cause the joint to become misshapen.
If you are experiencing pain or other problems in your feet, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for Bone Spurs May Include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and strength in the joint.
- Shoes: Wearing shoes with good arch support can help to reduce stress on the joint.
- Orthotics: Orthotics are inserts that can be placed in shoes to provide arch support and reduce stress on the joint.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the bone spur.
Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly People
Aging Process
The aging process can significantly affect the foot structure and function of older people, resulting in foot pain. As ligaments, tendons and arches in the feet weaken over time due to wear and tear, they may experience a reduced range of motion, making it more difficult to maintain balance. This can lead to an increased risk of falls and foot injuries. As people age, their feet go through a number of changes that can affect their health.
These Changes Include:
- Thinning skin: The skin on the feet becomes thinner and more fragile with age. This can make it more susceptible to cuts, blisters, and other injuries.
- Loss of fat and muscle tissue: The fat and muscle tissue in the feet also decreases with age. This can lead to changes in the shape of the feet and make them more prone to pain and discomfort.
- Decreased blood flow: The blood flow to the feet can also decrease with age. This can lead to cold feet and make it more difficult for the body to heal injuries.
- Changes in the bones and joints: The bones and joints in the feet can also change with age. This can lead to conditions such as arthritis, bunions, and hammertoes.
These changes can make it difficult for elderly people to walk, stand, and participate in activities that they enjoy. It is important for elderly people to take care of their feet and to see a doctor if they experience any pain or discomfort.
Here Are Some Tips for Elderly People to Take Care of Their Feet:
- Wash the feet daily with warm water and mild soap.
- Dry the feet thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize feet daily with a non-greasy lotion.
- Wear shoes that fit properly and have good arch support.
- Avoid walking barefoot on hard surfaces.
- See a doctor if your loved one experiences any pain or discomfort in her feet.
By following these tips, you help your elderly loved one keep their feet healthy and pain-free.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a prevalent condition among elderly people, and it can lead to various complications that cause foot pain. Diabetic neuropathy, for instance, may result in burning, tingling, or numbness in the feet, while poor blood flow increases the risk of infections and inflammation. Thus, it is crucial for older adults with diabetes to monitor their foot health regularly and consult a doctor when necessary. This chronic condition affects the way the body metabolizes sugar. People with diabetes have high levels of sugar in their blood, which can damage nerves and blood vessels throughout the body, including in the feet.
This Often Leads to a Number of Causes of Foot Problems in Elderly, Including:
- Neuropathy: Neuropathy is damage to the nerves that can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the feet. This can make it difficult to feel injuries, which can lead to infections.
- Angiopathy: Angiopathy is damage to the blood vessels that can cause poor circulation in the feet. This can make it difficult for the body to heal injuries and can lead to ulcers.
- Infections: People with diabetes are more likely to get infections, including in the feet. This is because high blood sugar levels can provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Amputation: Amputation is the removal of a body part, and it is a serious complication of diabetes. People with diabetes are more likely to have their feet amputated than people without diabetes.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet to prevent these problems.
Here Are Some Tips for People With Diabetes to Take Care of Their Feet:
- Wash your feet daily with warm water and mild soap.
- Dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize your feet daily with a non-greasy lotion.
- Wear shoes that fit properly and have good arch support.
- Avoid walking barefoot on hard surfaces.
- Check your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or redness.
- See a doctor if you experience any pain or discomfort in your feet.

Obesity
Carrying excess weight can put significant strain on the feet, especially in elderly people whose foot structures are already weakened by the aging process. Obesity can cause heel pain, arch pain, and inflammation, contributing to various conditions like plantar fasciitis and tendonitis. Obesity is a major risk factor for a number of health problems, including foot problems. While obesity might not be the first cause of foot pain in elderly people, it often leads to other conditions that affect the feet.
In Elderly People, Obesity Increases the Risk of Developing a Number of Foot Conditions, Including:
- Plantar fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is a condition that causes pain in the heel. It is caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot.
- Bunions: Bunions are a deformity of the big toe joint. They are caused by the big toe becoming misaligned and turning inward.
- Hammertoes: Hammertoes are a deformity of the toes. They are caused by the toes becoming bent at the middle joint.
- Charcot foot: Charcot foot is a condition that causes the bones in the foot to break down. It is caused by damage to the nerves and blood vessels in the foot.
- Ulcers: Ulcers are open sores that can develop on the feet. They are more likely to develop in people with diabetes or obesity.
These conditions can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty walking. In some cases, they can also lead to serious complications, such as infection or amputation.
There Are a Number of Things That Elderly People Can Do to Reduce Their Risk of Developing Foot Problems Related to Obesity, Including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Losing weight can help to reduce the stress on the feet and can help to prevent or improve foot problems.
- Wearing supportive shoes: Shoes that provide good arch support and cushioning can help to reduce stress on the feet.
- Avoiding high heels: High heels can put additional stress on the feet and can increase the risk of developing foot problems.
- Checking their feet daily: Elderly people should check their feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or redness. Any problems should be reported to a doctor promptly.

Infections
Foot infections, whether bacterial, or fungal infections, or viral, can cause pain and discomfort in older people. The risk of infections is higher if one’s immune system is compromised or in cases where underlying conditions like diabetes are present. A common infection associated with COVID-19, for example, can cause redness and inflammation in the feet.
Check toenails for ingrown toenails or nail disorders including infections. Older adults might have less feeling in their toes and might not notice ingrown toenails. They might not notice an ingrown toenail it becomes infected. Another cause of nail disorders is ill fitting footwear. Many foot problems in older adults can be prevented by well-fitted shoes. As people age, their immune system weakens, making them more susceptible to infections. These infections often become the cause of foot pain in elderly people.
There Are a Number of Things That Elderly People Can Do to Help Prevent Infections, Including:
- Washing their hands frequently: Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds is one of the best ways to prevent the spread of germs.
- Getting vaccinated: Vaccinations can help protect people from a variety of infections, including pneumonia, influenza, and shingles.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help boost the immune system and fight off infection.
- Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is important for overall health and can help the body fight off infection.
- Managing chronic conditions: People with chronic conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, are at an increased risk of infection. It is important to manage these conditions to reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoiding contact with sick people: If someone is sick, it is best to avoid contact with them to reduce the risk of getting sick.
- Seeing a doctor promptly: If someone develops any symptoms of infection, such as fever, chills, or a sore throat, it is important to see a doctor promptly. Early treatment can help prevent serious complications.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. It is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product that is produced when the body breaks down purines. Purines are found in certain foods, such as red meat, shellfish, and organ meats.
Gout is more common in elderly people. This is because the body’s ability to break down uric acid decreases with age. Gout can also be caused by certain medications, such as diuretics and aspirin.
Gout most commonly affects the big toe joint, but it can also affect other joints, such as the knees, ankles, and wrists.
The Symptoms of Gout Usually Come on Suddenly and Can Be Very Severe. They Include:
- Aching pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Heat
- Tenderness
The symptoms of gout usually last for a few days, but they can come back again if the uric acid levels in the blood are not controlled. These continue to cause foot pain in elderly loved ones util corrected.
There Are a Number of Things That Elderly People Can Do to Help Prevent Gout, Including:
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is low in purines can help to prevent gout.
- Drinking plenty of fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids can help to flush uric acid out of the body.
- Losing weight: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help to reduce your risk of gout.
- Taking medications: If you are at risk of gout, your doctor may prescribe medications to help lower your uric acid levels.
Subtalar Joint Dysfunction
The subtalar joint, located at the back of the foot below the ankle joint, allows the foot to move in various directions. Subtalar joint dysfunction refers to the abnormal movement or alignment of this joint and often causes significant pain, balance issues, and mobility problems in older individuals. Subtalar joint dysfunction can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the foot and ankle. It can also make it difficult to walk, run, and stand. The condition is more common in elderly people because the joints in the foot and ankle tend to become less flexible with age.
There Are a Number of Causes of Subtalar Joint Dysfunction, Including:
- Injury: An injury to the foot or ankle, such as a sprain or fracture, can damage the subtalar joint.
- Arthritis: Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. It can affect the subtalar joint, as well as other joints in the body.
- Degenerative changes: As people age, the tissues in the body, including the cartilage in the joints, tend to break down. This can lead to subtalar joint dysfunction.
There Are a Number of Treatments for Subtalar Joint Dysfunction, Including:
- Rest: Resting the foot and ankle can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Ice: Applying ice to the foot and ankle can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the foot and ankle with an elastic bandage can help to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the foot and ankle can help to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve the range of motion and strength in the foot and ankle.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the subtalar joint.
Heel Pain and Plantar Fasciitis
Heel pain is often attributed to plantar fasciitis, a condition that involves inflammation in the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes. Elderly people are at a higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis due to the natural weakening of this tissue over time, along with other factors like obesity and reduced mobility. Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that causes foot pain in elderly loved one’s heel. It is caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot.
Plantar fasciitis is more common in elderly people because the plantar fascia tends to become weaker and less flexible with age. It is also more common in people who are overweight or obese, people who have flat feet, and people who participate in activities that put a lot of stress on the feet, such as running and jumping.
The Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Include:
- Pain in the heel
- Pain that is worse in the morning or after periods of rest
- Pain that gets better with activity
- Swelling in the heel
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is usually made based on the patient’s history and physical examination. In some cases, the doctor may order an X-ray to rule out other conditions, such as a stress fracture.
There Are a Number of Treatments for Plantar Fasciitis, Including:
- Rest: Resting the foot can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Ice: Applying ice to the foot can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the foot with an elastic bandage can help to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the foot can help to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Stretching: Stretching the plantar fascia can help to improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Shoes: Wearing shoes with good arch support can help to reduce stress on the plantar fascia.
- Orthotics: Orthotics are inserts that can be placed in shoes to provide arch support and reduce stress on the plantar fascia.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to release the plantar fascia.
Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, which is the thick band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in elderly people.
There Are a Number of Risk Factors, That Can Contribute to Achilles Tendonitis, Including:
- Overuse: Achilles tendonitis is often caused by overuse, such as from running or jumping.
- Injury: An injury to the Achilles tendon, such as a tear or strain, can also lead to Achilles tendonitis.
- Degenerative changes: As people age, the Achilles tendon can become weaker and more susceptible to injury.
- Certain medical conditions: Achilles tendonitis is more common in people with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis.
The Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis Include:
- Pain in the back of the heel
- Swelling in the back of the heel
- Tenderness to the touch
- Inflammation
- Stiffness
The diagnosis of Achilles tendonitis is usually made based on the patient’s history and physical examination. In some cases, the doctor may order an ultrasound or MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
There Are a Number of Treatments for Achilles Tendonitis, Including:
- Rest: Resting the tendon is important to allow it to heal.
- Ice: Applying ice to the tendon can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the tendon with an elastic bandage can help to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the tendon can help to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Stretching: Stretching the tendon can help to improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Shoes: Wearing shoes with good arch support can help to reduce stress on the tendon.
- Orthotics: Orthotics are inserts that can be placed in shoes to provide arch support and reduce stress on the tendon.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and strength in the tendon.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the tendon.
The best treatment for Achilles tendonitis will vary depending on the severity of the condition. If you are experiencing pain or other problems with your foot, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Here Are Some Tips to Help Prevent Achilles Tendonitis:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Wear shoes with good arch support.
- Stretch your Achilles tendon regularly.
- Avoid activities that put a lot of stress on your feet.
- If you have pain, rest your foot and apply ice.
If you have any concerns about Achilles tendonitis, be sure to see a doctor.
Symptoms and Diagnosing Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly People
Clinical Examination
During a clinical examination, healthcare professionals may look for a range of symptoms in elderly patients’ feet. Common symptoms of foot pain include swelling, stiffness, redness, burning sensations, tingling, and numbness. Each of these symptoms can indicate various underlying causes of foot pain. For example, tingling or numbness may suggest nerve damage, while redness or swelling can indicate inflammation or an infection.
Additionally, other factors such as a patient’s medical history or specific physical activities may contribute to the development of foot pain. Elderly individuals with conditions like osteoporosis might experience a higher risk of foot fractures, potentially leading to pain and discomfort.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies play a crucial role in diagnosing the cause of foot pain. Healthcare professionals may use different types of imaging tests depending on the nature of the symptoms and the patient’s medical history. Common imaging studies for diagnosing foot pain include:
- X-rays: These images can help identify fractures, bone spurs, or abnormal bone structure, which might be causing the pain.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This imaging test provides detailed views of the soft tissues within the foot, including ligaments, muscles, and tendons. It can help in identifying conditions like tendonitis or torn ligaments.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans: A CT scan can offer a more comprehensive image of the foot, combining multiple X-ray images to create a three-dimensional view. This imaging method can also help spot fractures and other bone abnormalities.
By using clinical examinations and imaging studies, healthcare professionals can determine the cause of foot pain in elderly patients and devise appropriate treatment plans to alleviate the discomfort.
Treatment and Management, Find and Correct Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly Loved Ones
Conservative Approaches for Correcting the Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly People
Conservative approaches should be considered as the primary method in managing foot pain in elderly people since they typically have fewer complications and lower risks. These approaches include:
- Pain management: Utilizing over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation in the affected joints.
- Physical therapy: A certified physical therapist can recommend exercises to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility in the ankles, knees, and foot joints, which can reduce foot pain over time.
- Proper foot care: Maintaining good foot hygiene, regularly trimming toenails, and treating corns and calluses can prevent further complications and enhance overall foot health.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, conservative treatments may not provide sufficient relief for foot pain in elderly individuals. In these instances, surgical interventions could be considered to address specific issues such as hammertoe, severe bunions or other foot deformities. However, it is crucial to weigh the potential benefits of surgery against the risks, as elderly patients might face slower healing and higher rates of complications.
Footwear and Orthoses
Footwear and orthoses can play a significant role in managing and preventing foot pain in elderly people. Recommendations for footwear and foot orthoses include:
- Proper footwear: Selecting shoes that provide appropriate support, cushioning, and fit can help alleviate pressure on joints and reduce wear and tear on the feet.
- Orthotic devices: Custom-made foot orthoses can be beneficial in distributing pressure evenly across the foot and providing additional support for those with specific foot problems, such as flat feet or high arches.
- Footwear advice: Consulting with a podiatrist or an orthotist can ensure that the selected shoes and orthoses are suitable for the individual’s foot condition and specific needs.
By incorporating these treatments and management strategies, elderly individuals may experience fewer foot problems, ultimately leading to improved mobility and quality of life.

Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and preventing foot pain in elderly individuals. Including foods that are rich in essential nutrients and low in saturated fats encourages better joint and bone health. Limiting the intake of red meat and alcohol may help reduce inflammation in the body. Moreover, maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent obesity, which is known to contribute to foot problems and overpronation issues.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for elderly people to maintain strength, stability, and overall well-being. Activities such as walking and low-impact exercises help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls that may lead to foot pain. It is crucial to choose activities that don’t put undue stress on the ankles, wrists, and fingers. Some low-impact exercises that are beneficial for the elderly include:
- Swimming
- Walking
- Yoga
- Tai Chi
Routine Foot Care
Practicing routine foot care is vital in managing foot health and minimizing pain in older adults. Of course, elderly individuals need to wear comfortable, well-fitted shoes that provide adequate support and reduce pressure on the tendons and bones of the foot. In fact, ill-fitting shoes often inflict pain and lead to other problems.
Regular self-checks for any swelling, tenderness, or joint pain in the feet are necessary to identify potential issues early on. Consulting with a medical professional for adequate foot care guidelines and addressing any specific concerns may help prevent disabling foot pain and enhance the quality of life in elderly populations.
Emerging Research and Future Prospects for Correcting Causes of Foot Pain in Elderly
Recent studies have brought attention to the common issue of foot pain in elderly people. Several factors are associated with this type of pain, such as advancing age, sex, obesity, comorbidities, inappropriate footwear, and physical activity levels, among others 1. With the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, limited mobility, and restricted access to healthcare services may exacerbate foot pain and related conditions in older adults.
Research advancements have been instrumental in understanding the prevalence and impact of painful foot disorders in the geriatric population. One study found that frequent foot pain affects mostly the forefoot and toes, is more prevalent in women than men, and is at least moderately disabling in two-thirds of cases 2. Furthermore, foot pain may contribute to an increased risk of falls, affecting older adults’ quality of life and overall wellbeing 3.
Accurate Diagnosis
In light of these findings, experts have called for heightened awareness and improved management of foot pain in the elderly. Accurate diagnosis of the underlying causes of foot pain is crucial and can be achieved in most cases through clinical evaluation 4. The recognition and treatment of chronic foot pain can significantly improve older adults’ mobility, function, and general health.
Current health topics that may impact the future of foot pain research and management include the role of mental health, nutritional interventions, and personalized medicine approaches to alleviate and prevent foot pain in older populations. As our understanding of the relationship between these factors and foot pain deepens, healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions that cater to individual needs and optimize outcomes.
In conclusion, emerging research and future prospects in the field of foot pain in elderly people aim to enhance diagnostic accuracy, identify novel treatments, and address current health concerns relevant to this population. The continued collaboration of researchers, healthcare professionals, and affected individuals will be crucial for advancing knowledge and improving the quality of life for those experiencing foot pain.
Footnotes
Discover the Splendors of Aging: Connect, Engage, and Care Together!
Hey there, fellow seniors and caregiving enthusiasts! Looking for a place where you can find awesome content about geriatric conditions, elderly care, and product reviews? Look no further! Come join us on our social media accounts and be a part of our vibrant community at Florida Splendors.
On our Facebook page, we share engaging posts, informative articles, and heartwarming stories that will keep you connected and inspired. Head over to Instagram for beautiful visuals and snapshots of our favorite moments, and don’t forget to follow us on Twitter for real-time updates and insightful discussions.
Whether you’re seeking advice, looking for product recommendations, or simply want to connect with like-minded individuals passionate about geriatric care, our social media accounts are the place to be. So click those links, hit that follow button, and let’s embark on this amazing journey together. We can’t wait to connect with you!
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FloridaSplendors
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/floridasplendors/
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/floridasplendors
Twitter: https://twitter.com/FloridaSplendor
FAQs
As a caregiver, how can I help alleviate foot pain for the seniors under my care?
As a caregiver, you play a crucial role in ensuring the comfort and well-being of the seniors you care for. To alleviate foot pain, you can assist with gentle foot massages, encourage regular foot exercises, and help them wear comfortable and supportive footwear. It’s also important to ensure their feet are clean, dry, and well-moisturized to prevent skin issues. If the pain persists or worsens, it’s essential to seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Is it common for seniors to experience foot pain solely due to aging?
While foot pain can be more prevalent in seniors, it’s not solely attributed to aging itself. Factors such as wear and tear over the years, chronic conditions like arthritis, osteoporosis, or diabetes, and improper footwear choices can contribute to foot pain. Aging can also lead to changes in foot structure and decreased circulation, making the feet more susceptible to discomfort. Therefore, it’s crucial to address the specific causes of foot pain rather than assuming it’s solely a result of aging.
Can foot pain in seniors be aggravated by certain activities or lifestyle choices?
Absolutely. Certain activities and lifestyle choices can worsen foot pain in seniors. Prolonged periods of standing or walking, wearing ill-fitting shoes or high heels, excessive weight-bearing activities, and lack of regular exercise can all contribute to foot discomfort. It’s important to encourage seniors to maintain a healthy weight, engage in low-impact exercises like walking or swimming, and wear properly fitting shoes with good arch support. These choices can help alleviate foot pain and promote overall foot health.
Are there any natural remedies or alternative therapies that can help relieve foot pain in seniors?
There are several natural remedies and alternative therapies that can provide relief for foot pain in seniors. These include applying ice packs or warm compresses, soaking feet in Epsom salt baths, using over-the-counter pain-relieving creams or gels, and exploring complementary treatments like acupuncture or reflexology. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new remedies or therapies, as they can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific condition causing the foot pain.