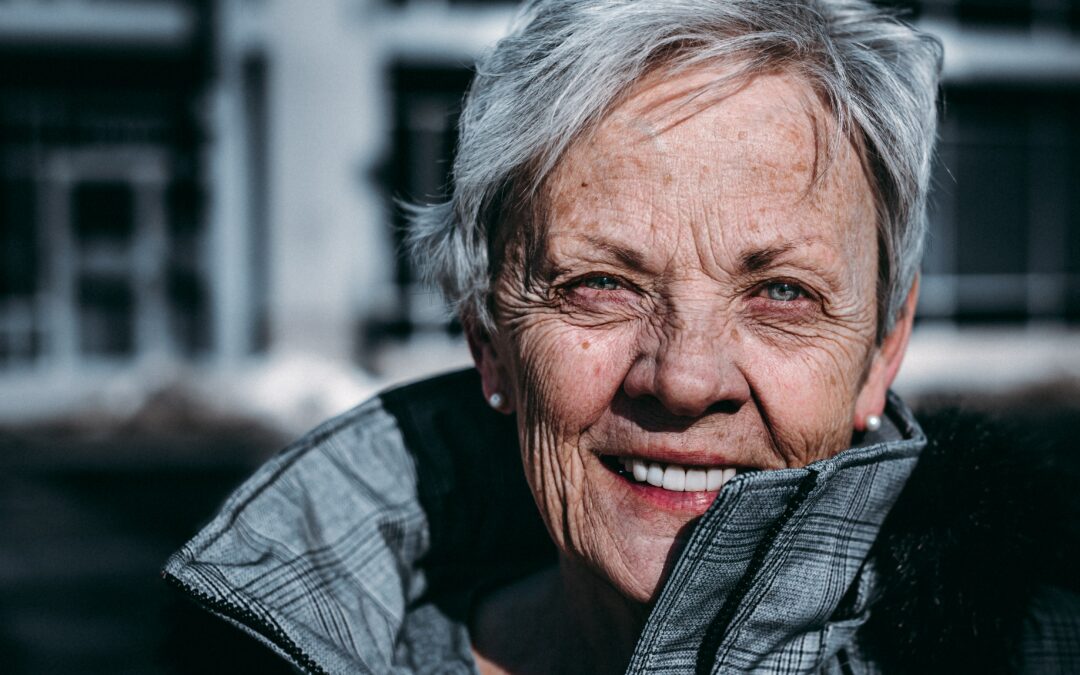
Have you ever wondered if thinner skin is a normal part of aging? Is there any treatment for thin skin, and can you make it thicker? Well, the answer is yes!
Specific steps can help you maintain plump and beautiful skin in your 30s, 40s, and 50s.
But before you take offense, let me clarify! I’m not talking about your ability to handle criticism; I’m addressing the literal thinning of your skin with each passing day.
Thin skin is not just about looks but is also a key factor for your health. Your skin is your first defense against pathogens, toxins, UV rays, and the extremities of temperature.
As it thins, it loses some of its abilities, making you less sensitive to touch and more vulnerable to environmental stress.

Image by Freepik
Thinning skin with age comes with a unique set of challenges. It makes older adults more vulnerable to cuts, bruises, and scrapes that often go unnoticed until after the fact. Beyond cosmetic worries, friable skin also raises the risk of infections and health complications.
However, fear not! While we can’t turn time back, it is possible to slow the thinning process. Simple habits, boosting Collagen, and treatment for thin skin can make a big difference.
So, Stick with us as we spill the beans on how to keep your skin firm and looking good, no matter how many candles are on your birthday cake!
Contents
What is Thinning of the Skin?
Thinner or friable skin is more prone to tears, bruises, or breaks. Thinning skin with age is common in older adults. In some cases, the skin develops an appearance like tissue paper, called crepey Skin.
This condition is common in older adults and is mainly noticeable on the face, arms, and hands. People with thin skin might observe that veins, tendons, bones, and capillaries become visible beneath the skin in these areas.
Our skin has many layers. The middle layer is called the dermis, contributing to 90 percent of our skin’s thickness. The dermis comprises Collagen and elastin, providing skin strength, flexibility, and elasticity. When thin skin develops, it results from the dermis thinning out. Moreover, many link thinning skin with age. However, it can also result from UV exposure, genetics, lifestyle, and certain medications. Thus, understanding the causes of thin skin can help you better care for your health.
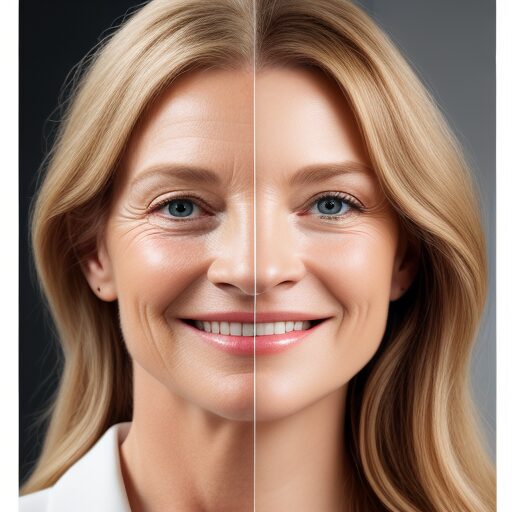

Symptoms of Thinning Skin with Age
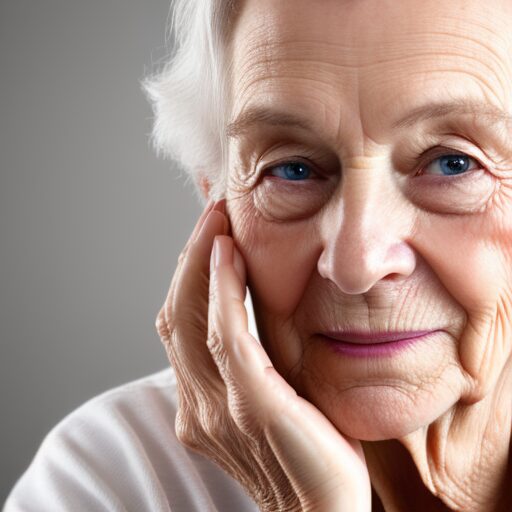

Thin skin symptoms are distinctive and often manifest in various noticeable ways. Some common indicators include:
Translucency: Thinning Skin tends to become more translucent. It makes blood vessels, tendons, and bones visible beneath the skin. This is particularly apparent if you experience thinning hands and arms.
Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Reduced skin thickness causes fine lines and wrinkles, especially on the face. These lines may be more pronounced, and the skin may appear more delicate.
Increased Fragility: Thin Skin also tends to be more fragile. It makes your skin more susceptible to tears, cuts, and bruises. Even minor impacts that might not have caused issues before can lead to visible damage.
Slow Healing: Thin Skin often takes longer to heal. Wounds, cuts, or bruises may take longer for the skin to recover, and there is an increased risk of scarring.
Visible Veins: As the Skin loses thickness, veins close to the surface become more visible. This is commonly observed on thinning hands and arms.
Crepey Texture: With age, thin skin can develop a texture resembling crepe paper with fine, crinkled lines. This is often seen on the arms and other areas with reduced skin thickness.
Identifying these thinning skin signs is crucial for elderly individuals and their caregivers. It can help you protect the skin, prevent injuries, and promote skin health in aging. In addition, regular skin care, sun exposure, and a healthy lifestyle can also help you retain your skin’s integrity as you age.
Causes of Thinning of the Skin in Older Adults

Image by Freepik
Thinner skin in older people can be a result of a variety of causes, often resulting from a mix of factors. Here are some common contributors to the thinning of the skin with age:
Natural Aging Process
As we age, our skin naturally changes. Collagen and elastin, vital for skin strength, drop over time, making our skin thinner. These proteins act like the building blocks, providing firmness and stretchiness. With their reduction, our skin becomes more prone to sagging and thinning. Understanding these natural changes can help you better care for your skin as you age.
Reduced Sebum Production within the Body
Our skin needs a natural oil called sebum to maintain moisture and suppleness. The sebaceous gland within the skin produces sebum. However, as we age, the production of sebum drops, resulting in drier skin. It increases the risk of thinning skin, making our skin more prone to bruises, cuts, and scrapes.
Prolonged Sun Exposure
As we age, our skin becomes susceptible to various forces, including sun and harsh weather. Prolonged exposure to UV rays triggers the breakdown of Collagen and elastin in our skin. The process is also known as photoaging. It contributes to the thinning of the skin and the development of wrinkles and fine lines.
Genetic Factors
The genes we inherit from our family also have a say in how our skin turns out, including how thick it is. Some might have thinner skin as they age because of their family history.
It is like a unique plan for how our skin will change as we age. Knowing about this family influence helps us understand why some people may have thinner skin as they age. It is like a unique code in our genes that determines how thick our skin will be as we age.
Poor Intake of Nutritional Supplements
Insufficient nutrition affects skin health, influencing its structure and function. Essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals are the building blocks for healthy skin. For example, vitamin C from fruits and vegetables aids collagen production and maintains skin firmness. In addition, Vitamin E, found in nuts and seeds, acts as an antioxidant, shielding the skin from damage.
Similarly, Omega-3 fatty acids present in fish support skin health. Older adults with thinner skin should include meat, nuts, and legumes in their diet for zinc. Inadequate intake of these essential nutrients aids in the risk of skin thinning.
Smoking
Smoking is also linked to the accelerated aging of the skin. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke wreak havoc on two essential proteins, Collagen and elastin. While Collagen maintains firmness of the skin, elastin imparts flexibility.
The hurtful effects of smoking on these proteins may also lead to premature thinning and wrinkles. Smoking speeds up how fast our skin ages, quickly losing its youthful qualities.
This isn’t just about looks; it also affects the health of our skin. So, avoiding smoking is vital if you want your skin to stay healthy and beautiful.
Use of Steroid Creams
Some people turn to anti-aging creams in the pursuit of a youthful appearance. While these creams offer temporary benefits, they are damaging our skin cells. Steroid creams reduce fine lines and add a youthful glow for a short time. However, the long-term effects are critical to consider.
Some anti-aging creams have ingredients that, over time, may have adverse effects on the skin. Prolonged use could result in irritation, sensitivity, or even thinning of the skin. Additionally, dependency on these creams may inhibit the skin’s natural processes.
Thus, being careful with these creams and sparingly relying on them is essential. Taking care of your Skin with a healthy lifestyle is a better way to keep it looking good for the long haul.
Other Medications
Certain medications may also cause thinning of the skin as a side effect. This is common with medics called topical steroids, which you use right on your skin.
These medicines usually come as a cream or ointment and are used to treat skin issues like eczema. While they can be helpful for specific skin problems, prolonged use might have a downside.
These meds are like a trade-off: they might help to treat specific skin issues, but you must be cautious as they could damage skin cells.
Video Credit: Doctors’ Circle World’s Largest Health Platform
Treatment for Thin Skin in the Elderly
If you already have thin skin, restoring that teenage glory might not be possible. However, there is a treatment for delicate skin to maintain its flexibility.
First, moisturizing is essential. Make sure to keep your skin moisturized as it keeps your skin hydrated and more resilient. Moreover, anything that causes redness or soreness harms your skin cells. Those with brittle skin should steer clear of harsh chemicals. Ensure protective gear like long sleeves is used to prevent bruising or damage.
In addition, a thin skin cream with vitamin A, like retinoids, may help reduce further thinning. While research suggests that retinol could normalize skin thickness, It may not suit all skin types. So, be sure to check with your doctor before using it.

Although collagen boosters’ impact on the skin isn’t proven, some individuals find them beneficial. A balanced diet of veggies, fruits, proteins, and whole grains aids overall health. In addition, foods with Vitamin E, like almonds and avocados, also help skin health and suppleness. Lastly, drink enough water to stay hydrated. Remember that dry skin is more susceptible to irritation and damage while being less flexible.
How to Prevent Thinning Skin with Age?
Aging is natural; signs like fine lines and thinner and drier skin happen as we age. While we cannot stop aging altogether, there are things we can do to slow it down and lessen its effects.
- Dress Smart: Covering up is always in style, whether you prefer a chic or casual look. Opt for long pants, sleeves, and a wide-brimmed hat. Wear gloves when driving and consider layering up when working outdoors.
- Enjoy the Shade: Arrange your schedule to spend the hottest hours indoors or in the shade. Protecting yourself from direct sunlight helps keep your skin happy and healthy. You may also want to use SPF 30 or higher sunscreen that shields from UVA and UVB rays.
- Daily Skincare Routine: No matter your age, taking care of your skin is crucial. Implement a daily skincare routine by moisturizing and using specialty products for different skin areas—face, body, neck, and chest. When using face masks, choose gentle ones on your skin to avoid face mask acne.
- Keeping skin Moisturized: keeping your skin moist is essential. It helps prevent dryness and damage by retaining water in the skin. Hydrated skin is more elastic and healthier.
- Avoid Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol dries out the skin. Thus, avoid excessive drinking and drink a glass of water between alcoholic drinks.
By taking these simple steps, you can take better care of your skin and keep it in its best possible shape.
Can Thinner Skin Be Thickened?
Even though you can’t wholly undo thinning skin, there are ways to make it thicker. The key is boosting Collagen, fixing elastin, and improving your skin. However, the most important thing is to keep your skin from getting even thinner by following the earlier tips. Here are some options for making your skin thicker:
- Topical Products: Look for thin skin products with retinol (Vitamin A). Retinol is a good choice, known for remodeling collagen, improving texture, and thickening skin cells.
- Laser Treatments: These treatments use lasers to stimulate collagen growth, making the skin layer stronger. However, take good care of your face after laser treatment.
- Radiofrequency and Ultrasound Therapy: These therapies use waves to heat the skin, promoting Collagen for firmer, smoother skin.
- Medical-Grade Skincare: Choose skincare products with proven ingredients that boost elastin and Collagen.
Is Sunlight Bad for Your Skin?

Harmful UV rays are the biggest culprits of thinning skin with age. UV rays can damage Collagen and elastin, aiding skin strength and elasticity.
Sunlight can harm the proteins, Collagen, and elastin in our skin, which give it strength and elasticity. Collagen makes our skin firm, while elastin lets it stretch and return to its original shape. Our skin becomes thinner and less bouncy when the sun damages these proteins. This process is often linked to fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of skin thickness.
It is vital, especially for older people, to protect their skin and prevent it from getting thinner due to sunlight. Here are some ways to do that:
- Use Sunscreen: Put on a broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect your skin from the sun.
- Stay in the Shade: Avoid direct sunlight, especially during the warmer sun hours.
- Wear Protective Clothes: Use long sleeves, pants, and hats with wide brims to shield your skin from the sun.
These tips can keep your skin healthy and reduce the effects of sun-induced aging.
Wrapping Up: Thinning Skin with Age
That is all about the thinning of the skin with age. Aging changes our skin, and thinning is a natural part of it. We may not completely stop these changes, but there are things we can do to keep our skin healthy. Simple steps like protecting our skin from the sun, skincare routines, and healthy choices can make a big difference.

Moreover, understanding why skin thins can help you better care for your skin. Wearing sunscreen, using good skincare, and living a healthy life can slow down aging.
Remember, aging is not just about how we look but about the experiences and wisdom we gain. So, as we care for our skin, let it reflect a life well-lived, full of stories and beauty.
FAQs
What is the best treatment for the fragile skin of older adults?
Taking care of older adults’ fragile skin involves a few vital steps. For example, you can use gentle skincare routines and moisturize with products with hyaluronic acid and ceramides. This helps keep the skin hydrated and firm. Also, it is crucial to protect the skin from the sun by using sunscreen and not staying in it too much. Moreover, eating a healthy diet with many antioxidants is another way to keep the skin healthy. See your doctor or a skin expert for personalized advice if you need help determining what’s best for your skin.
How does prolonged sun exposure contribute to skin aging?
Sun exposure can speed up skin aging by breaking down Collagen and elastin. UV rays also trigger the production of free radicals, causing cellular damage. A few steps can help to protect your skin from sun damage. First, wear sunscreen with a high SPF and protective clothing. Second, seek shade during peak sunlight hours. In addition, adopt a skincare routine that includes moisturizing and antioxidant-rich products. Moreover, stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, and avoid smoking, as these lifestyle choices play a role in maintaining skin health.
Is toner beneficial for aging skin?
Yes, using a toner can be good for thin skin in the elderly. A quality toner can help you balance the skin and eliminate leftover dirt. In addition, it prepares your skin to soak in moisturizers better. Look for toners with hyaluronic acid and antioxidants. These ingredients can hydrate your skin, protect it, and help with fine lines. Moreover, adding an excellent toner to your skincare routine boosts your skin for a youthful look. It’s a simple step that can make a noticeable difference in your complexion.
What are the best treatments for thin skin in the elderly?
Treatment for thin skin depends on why it is happening. However, using products with retinoids can help make your skin thicker over time. In addition, protecting your skin from sun damage is also vital, as sunlight can worsen thin skin. Moreover, moisturizers with hyaluronic acid can keep your skin hydrated. It is a good idea to talk to a skin doctor (a dermatologist) for advice tailored to you. They might suggest treatments like laser therapy or special injections. By taking care of your skin and getting expert advice, you can make thin skin better.
How should I choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen for the thinning of the skin?
To pick the right sunscreen for thinning skin, choose a broad-spectrum one with at least SPF 30. It would be best to look for zinc oxide or titanium dioxide in the ingredients, as these are gentle. Get a sunscreen labeled “fragrance-free” and “hypoallergenic” to avoid irritation. It’s good if it has moisturizing like hyaluronic acid for extra skin hydration. Put it on well and reapply every two hours, more if you are sweating or swimming. Check with your skin doctor if you cannot decide which is best. They can help you find the perfect sunscreen for your skin.
Welcome to Senior Parents!
Dive into a world of tips for a graceful golden era, heartwarming stories, and the best care for your loved ones.
Be part of our lively community, where aging is an art! We are your go-to source for regular updates on senior well-being.
Connect with us on social media for daily inspiration, laughter, and shared wisdom.
Together, let’s steer the aging journey with grace and celebrate the unique joys it brings. Join us in making the golden years truly special!
Follow, share, and connect with a community that understands and appreciates the beauty of aging.
Facebook: www.facebook.com/sr.parents
Insta: www.instagram.com/seniorparents/
Pinterest: www.pinterest.com/seniorparents/
Twitter: twitter.com/senior_parents
You Might Also Like the Following: