Diabetic Neuropathy is a condition that affects many seniors, particularly those living with diabetes. It occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels damage the nerves, leading to a range of foot-related issues. As seniors and caregivers, it’s essential to grasp the significance of this condition and its impact on the quality of life for older individuals.

Foot problems resulting from diabetic neuropathy encompass various issues, such as poor blood flow, nerve damage, and the development of foot ulcers. These complications can have severe consequences if left unattended. Thus, it is vital to stress the importance of proactive foot care to prevent potential complications.
This blog aims to provide seniors and their caregivers with a comprehensive roadmap for navigating the complexities of diabetic neuropathy-related foot problems. By addressing these concerns methodically, older individuals, healthcare professionals, and caregivers can gain valuable insights into effectively managing and reducing the risks associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Contents
Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a debilitating complication of diabetes that affects the nerves, particularly those in the extremities. This condition can lead to a range of foot problems caused by diabetic neuropathy, including poor blood flow, nerve damage, and foot ulcers. This section will delve into a comprehensive understanding of diabetic neuropathy, its types, causes, symptoms, progression, and the critical importance of early detection.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common types of diabetic neuropathy. It primarily affects the nerves in the arms, legs, feet, and hands. This condition can result in numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the affected areas. In severe cases, it can lead to serious complications like foot ulcers.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy involves damage to the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions, including blood pressure regulation and digestion. It can lead to poor blood flow, digestive and kidney diseases, and other systemic issues that affect overall health.
Focal Neuropathy
Focal neuropathy, or mononeuropathy, typically affects a single nerve or a specific group of nerves. It can cause sudden and severe pain in isolated areas, often leading to serious foot complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of diabetic neuropathy is prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels. People with diabetes are particularly susceptible to this condition, especially if their blood sugar levels are uncontrolled. Other risk factors include:
- High blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure can contribute to poor blood flow and exacerbate nerve damage.
- Smoking: Smoking can further reduce blood circulation and increase the risk of foot problems.
- Kidney diseases: Diabetes-related kidney issues can worsen nerve damage and foot complications.
- Poorly fitting shoes: Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes can cause pressure points and lead to serious foot problems.
- Risk factors: Genetics and family history can affect an individual’s susceptibility to diabetic neuropathy.
Symptoms and Progression
Diabetic neuropathy often starts with mild symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the extremities. As it progresses, symptoms may become more severe and debilitating, including:
- Foot ulcers: Persistent numbness can lead to unnoticed injuries that evolve into foot ulcers, which can become infected and difficult to heal.
- Charcot foot: This condition, characterized by bone and joint damage in the feet, can result in severe deformities.
- Peripheral arterial disease (PAD): Poor blood flow can lead to PAD, causing pain and cramping in the legs during physical activity.
- Serious foot complications: Untreated diabetic neuropathy can result in serious complications that may require amputation.
Importance of Early Detection
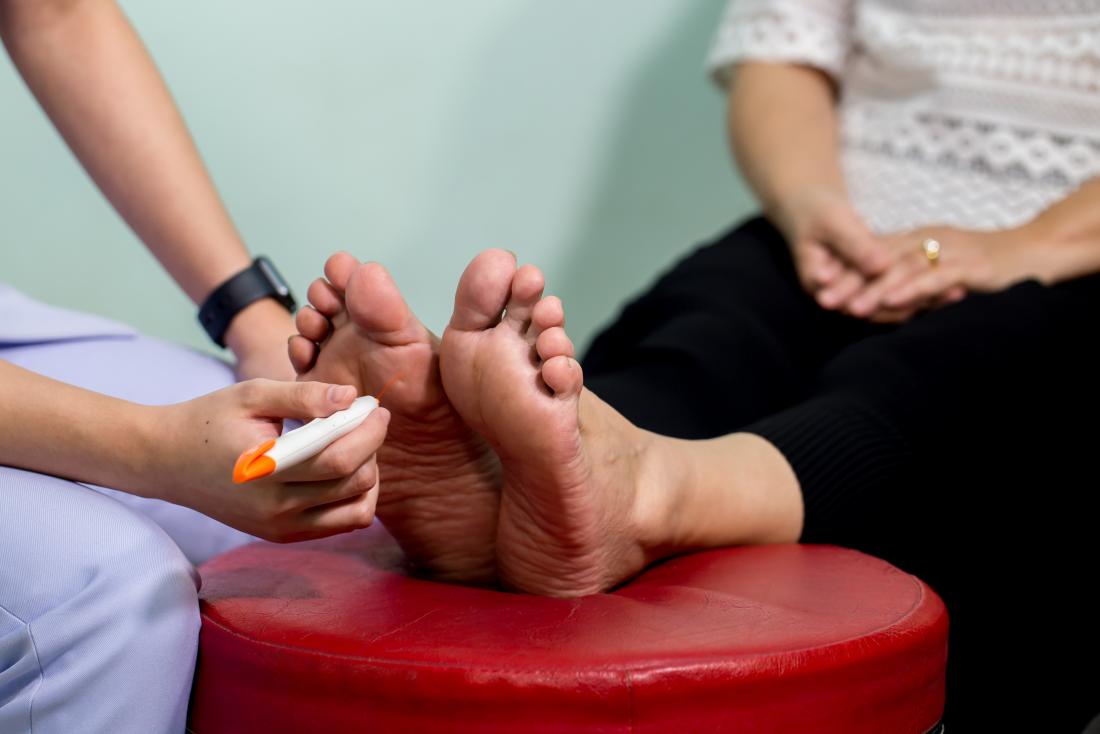
Early detection and intervention are paramount in managing diabetic neuropathy effectively. Regular foot exams, thorough foot care, and monitoring of blood glucose levels are essential to identifying potential problems early. Diabetic patients must also wear proper footwear, avoid tight socks, and maintain good foot hygiene to reduce the risk of foot complications.
Foot Problems Associated with Diabetic Neuropathy
Foot issues can be a frequent and potentially severe concern for seniors with diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy is a condition marked by nerve damage brought about by elevated blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. This nerve damage can impact multiple body areas, including the feet, often resulting in an array of foot problems and related complications. Grasping these challenges is pivotal for successfully managing and preventing such issues.
Neuropathic Ulcers
Neuropathic ulcers, also known as diabetic foot ulcers, are one of the most concerning complications of diabetic neuropathy. These ulcers are open sores that typically occur on the bottom of the feet. They develop due to nerve damage, poor blood flow, and repetitive pressure on specific foot areas. Let’s delve deeper into the causes and risk factors of neuropathic ulcers.
Causes
- Nerve Damage: Diabetic neuropathy impairs the sensation in the feet, making it difficult for individuals to detect injuries or pressure points that could lead to ulcers.
- Poor Blood Flow: Diabetic neuropathy can also affect the small blood vessels that supply the feet, reducing blood flow and impairing the body’s ability to heal wounds.
- High Blood Sugar: Elevated blood sugar levels can interfere with the body’s natural wound-healing processes, making it harder to recover from injuries.
The complications associated with neuropathic ulcers are significant and can lead to serious infections, tissue death, and even the need for amputation. Therefore, early detection, regular foot inspections, and proper foot care are crucial for preventing and managing neuropathic ulcers in individuals with diabetic neuropathy.
Charcot Foot
Charcot foot, also known as Charcot neuroarthropathy, is another severe foot problem that can occur in individuals with diabetic neuropathy. This condition involves the weakening and fracturing of bones in the foot due to nerve damage. Charcot foot often develops gradually, and its causes and consequences are noteworthy.
Causes
- Nerve Damage: Diabetic neuropathy can disrupt the normal nerve signals responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of the foot. As a result, individuals with Charcot’s foot may not feel pain or be aware of the damage occurring.
- Repetitive Stress: The combination of nerve damage and continuous stress on the foot from walking can lead to fractures and joint deformities.
- High Blood Sugar: Elevated blood sugar levels can weaken bones and connective tissues.
Charcot foot can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages because it often presents without obvious symptoms. However, if left untreated, it can lead to severe deformities, chronic pain, and disability. Management strategies include immobilization, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Early detection and prompt intervention are essential to prevent long-term complications.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a condition that often coexists with diabetic neuropathy and can exacerbate foot problems in individuals with diabetes. It involves the narrowing or blockage of arteries that supply blood to the extremities, including the legs and feet.
Causes
- Blood Vessel Damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the walls of blood vessels, accumulating plaque (atherosclerosis) and reducing blood flow.
- Poor Circulation: Reduced blood flow deprives the feet of essential nutrients and oxygen, making it challenging for the body to heal and resist infections.
- Risk Factors: PAD risk factors in people with diabetes include smoking, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels.
PAD can manifest with symptoms such as leg pain, cramping, and cold feet. In severe cases, it can lead to non-healing ulcers and even gangrene. Early diagnosis through methods like Doppler ultrasound and appropriate management, including lifestyle changes and vascular interventions, can help mitigate the impact of PAD on foot health.
Calluses and Corns
Calluses and corns are common foot problems that can be particularly troublesome for individuals with diabetic neuropathy. These conditions involve thickening skin layers in response to pressure or friction and can indicate poor-fitting footwear or abnormal foot mechanics.
Causes
- Poorly Fitting Shoes: Wearing shoes that do not fit properly or exert excessive pressure on specific feet areas can lead to calluses and corns forming.
- Reduced Sensation: Diabetic neuropathy diminishes the ability to perceive discomfort, making it difficult for individuals to identify and address issues related to ill-fitting shoes or pressure points.
Calluses and corns may seem relatively benign but can develop into serious foot complications, especially if they become ulcerated or infected. Proper footwear, regular foot inspections, and early intervention, such as professional podiatric care, are essential for managing and preventing these issues in individuals with diabetic neuropathy.
Preventive Measures for Foot Problems Caused by Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, affecting millions of people worldwide. One of the most vulnerable areas for individuals with diabetic neuropathy is their feet. The combination of nerve damage, poor blood flow, and high blood sugar levels can lead to serious foot complications, including ulcers, infections, and even amputations. However, various preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of these complications.

Foot Care Education
Foot problems caused by diabetic neuropathy are often the result of a lack of awareness and education. People with diabetes may not fully understand the importance of foot care and the potential consequences of neglecting it. Foot care education is a critical component of preventive measures.
Proper education should cover:
- The importance of daily foot inspections.
- The necessity of keeping feet clean and dry.
- The significance of moisturizing but avoiding between the toes.
- The dangers of walking barefoot.
- The benefits of regular professional foot check-ups.
- The need to seek immediate medical attention for any foot issues.
By providing comprehensive foot care education, individuals with diabetic neuropathy can proactively manage their foot health and prevent complications.
Regular Foot Inspections
Regular foot inspections are fundamental to foot care for people with diabetic neuropathy. Individuals should be encouraged to inspect their feet daily. Key points to emphasize include:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the feet for any signs of injury, cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling. Any unusual changes should be reported to a healthcare professional immediately.
- Sensory Check: Test the sensation in the feet by gently touching various areas with a soft object (e.g., a cotton ball). Loss of sensation may indicate nerve damage and requires medical attention.
- Toenail Care: Trim toenails straight across to prevent ingrown toenails, but avoid cutting them too short.
- Foot Temperature: Use the back of your hand to feel temperature differences between feet. An unusually warm or cold foot may indicate circulation problems.
- Footwear Assessment: Check shoes for foreign objects or rough spots inside that could cause irritation or injury.
Regular foot inspections empower individuals to detect problems early and seek timely treatment, reducing the risk of serious complications.
Proper Footwear
Choosing the right footwear is crucial for individuals with diabetic neuropathy. Ill-fitting or inappropriate shoes can lead to pressure sores, blisters, and other foot problems. Key considerations for proper footwear include:
- Comfortable Fit: Shoes should fit well and provide ample cushioning to reduce pressure on sensitive areas.
- Supportive Soles: Opt for shoes with arch support and cushioned insoles to minimize foot stress.
- Breathability: Choose breathable materials to keep feet dry and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
- Protective Toe Box: Look for shoes with a spacious toe box to prevent crowding and friction.
- Avoid High Heels: High heels can increase pressure and instability, so it’s best to avoid them.
- Regular Replacement: Replace worn-out shoes to ensure they provide adequate support and protection.
Proper footwear can help individuals with diabetic neuropathy maintain healthy feet and reduce the risk of foot problems.
Glycemic Control
Blood sugar control is paramount in preventing diabetic neuropathy and its associated complications, including foot problems. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, increasing the risk of neuropathy and poor circulation. Key measures for glycemic control include:
- Medication Adherence: Take prescribed diabetes medications as a healthcare provider directs.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly check blood sugar levels and follow recommended monitoring schedules.
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a balanced diet focusing on complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and fiber-rich foods.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity as a healthcare provider recommends to help manage blood sugar levels.
- Consultation with Healthcare Team: Regularly consult with healthcare professionals to adjust medications and treatment plans.
Smoking Cessation
It is a significant risk factor for poor circulation and vascular damage, which can exacerbate foot problems in individuals with diabetic neuropathy. Smoking cessation is a critical preventive measure. Encourage individuals to seek support and resources for quitting smoking, such as counseling and nicotine replacement therapy.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight benefits overall health and can reduce the risk of foot problems associated with diabetic neuropathy. Excess weight can put additional stress on the feet and worsen neuropathic symptoms. Weight management strategies may include:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on portion control and choosing nutrient-dense foods.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity supports weight loss and improves overall health.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Seek guidance from a healthcare provider or dietitian for personalized weight management plans.
Video Credit: @activeseniorshealthcentre5252
Taking Control of Your Foot Health in Diabetic Neuropathy
As we wrap up our discussion on managing foot problems caused by diabetic neuropathy, it’s crucial to remember that seniors and caregivers play a pivotal role in this journey. Taking proactive steps is the name of the game. We all know that poor blood flow and blood sugar issues are all too common among seniors with diabetes, and they can lead to some pretty serious foot complications.

Think about it: diabetic foot problems encompass nerve damage, foot ulcers, and infections. That’s why the American Diabetes Association makes such a big deal about proper foot care. It’s not just about choosing the right shoes; it’s also about avoiding those tight socks that can cause trouble. Don’t hesitate to contact foot doctors and foot and ankle surgeons when you need their expertise.
Refrain from letting Charcot foot and thorough foot exams slip your mind. They’re a big deal regarding foot health, especially for seniors. High blood pressure and uncontrolled blood sugar levels can increase the risk of complications, but you can make a real difference with early intervention and careful monitoring.
So, the bottom line is that foot health is a big deal, and it can seriously impact overall well-being, especially for seniors with diabetic neuropathy. With some watchful eyes, a commitment to good foot care habits, and a willingness to follow medical advice, you can reduce the risk of severe foot complications and take control of your health. Just remember, the ball is in your court when it comes to your feet and your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common foot problems caused by diabetic neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy can lead to various foot problems, including nerve damage, ulcers, and poor blood flow.
How can people with diabetes manage their foot problems effectively?
Managing foot problems involves maintaining blood sugar levels, regular foot exams, and wearing proper footwear as recommended by the American Diabetes Association.
What are the serious complications associated with diabetic foot problems?
Serious complications may include Charcot foot, poor circulation, and severe infections, leading to tissue death and even amputation.
What role do foot doctors and ankle surgeons play in diabetic foot care?
These specialists provide essential care, including thorough foot exams, surgical interventions, and advice on preventing further complications.
How can individuals reduce the risk of diabetic foot problems and maintain overall health?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as wearing shoes that fit well, avoiding tight socks, and practicing good foot care, can help prevent complications and promote foot health.
Join Our Thriving Senior Care Community on Social Media!
Are you passionate about seniors and caregiving? Looking for a supportive community and valuable resources? Look no further!
? Engaging Content: Explore informative articles, heartwarming stories, and helpful tips. ? Product Reviews: Get the lowdown on senior care products to make informed choices. ? Community Connection: Connect with like-minded individuals who share your enthusiasm for senior care.
Find us on your favorite platforms:
? Facebook: Dive into discussions and updates on our Facebook Page.
? Instagram: Follow us for inspiring visuals and stories on Instagram.
? Pinterest: Discover a treasure trove of ideas and resources on Pinterest.
? Twitter: Stay updated with news and insights on Twitter.
Don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter for the latest insights and updates – it’s your key to staying informed and connected with our wonderful community!”