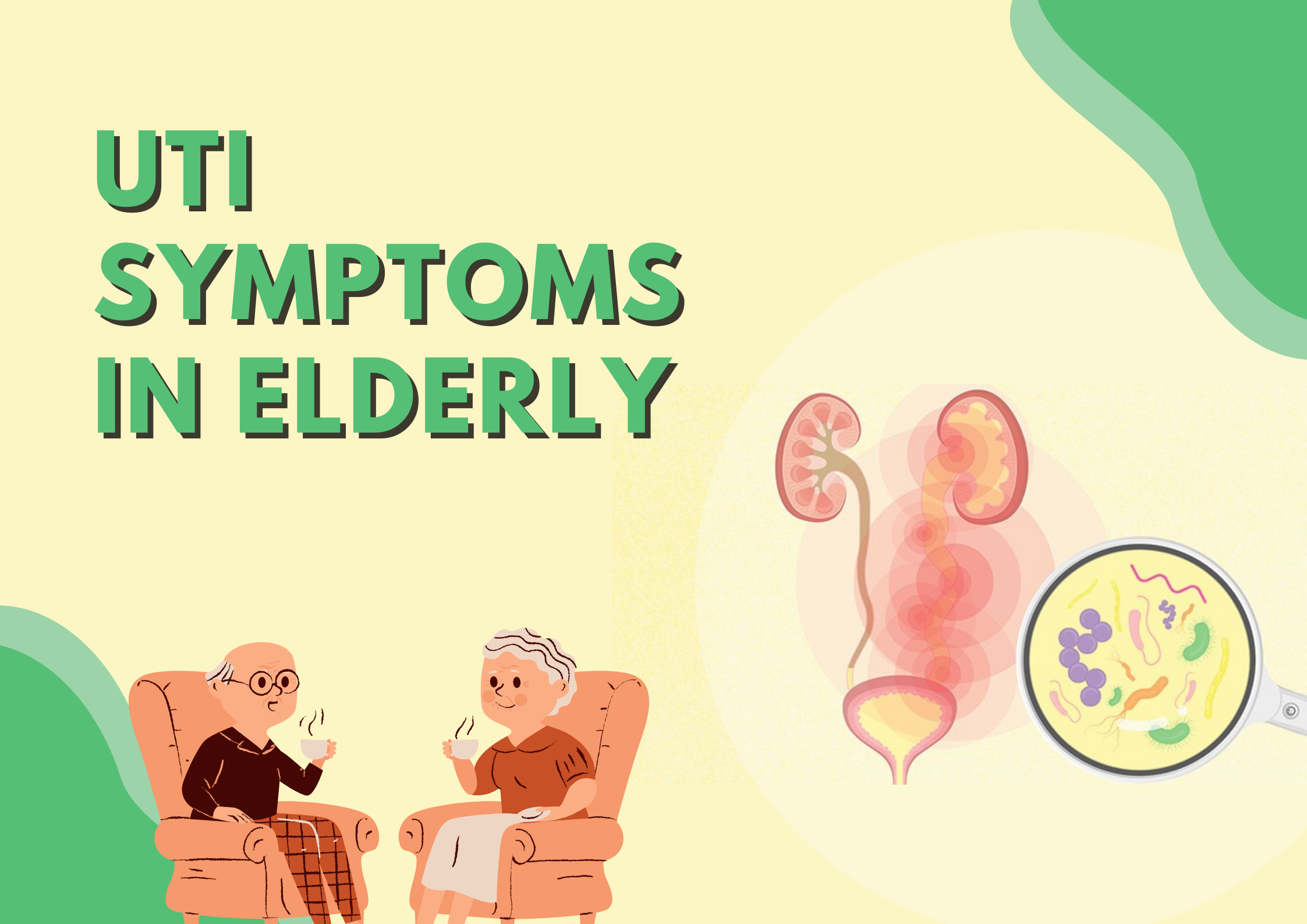
Taking care of the elderly is a challenging task, especially when it comes to their health. One common problem that seniors face is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI). UTIs in the elderly can lead to severe complications if not detected and treated on time. Thus, recognizing UTI symptoms in elderly is crucial.
As a caregiver, it’s crucial to understand UTI symptoms in the elderly and know how to respond appropriately. In this blog, we provide you with a comprehensive guide on UTI symptoms in the elderly and what you can do about them.
We also explore why they are more susceptible to UTIs and the risks and complications involved. Lastly, we’ll explain how you can reduce the risk of UTIs through preventive measures, including diagnosis and treatment options available for your loved ones.
Contents
Understanding UTI in the Elderly:
A Brief Overview
UTIs are common infections in older adults, particularly women, due to changes in urinary tract function and the immune system. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and hospitalization.
UTIs can lead to severe symptoms in elderly if left untreated. Caregivers play a vital role in recognizing signs of UTIs in the elderly. Prompt action is necessary to ensure the well-being of older people.

Why Elderly Individuals are More Susceptible to UTIs
Age-related changes in the urinary tract, such as an enlarged prostate in men, can increase the risk of UTIs in older individuals. Certain medical conditions, like kidney damage or urinary catheters, also make them more susceptible to urinary tract infections.
Hormonal changes, such as menopause in women, can affect the vaginal microbiome, further increasing the risk. Additionally, the weakened immune system in older adults leaves them more vulnerable to infections, including UTIs. Poor hygiene, dehydration, and frequent urination are common risk factors for UTIs in the elderly.
Credits: North Star Senior Advisors
Empower elderly UTI relief with our specialized Cranberry Supplement, fortified with 900 mg of Cranberry fruit extract and immune-boosting Vitamin C. Combat urinary tract discomfort effectively and proactively support overall well-being. Elevate their health journey with our premium formula! #ads #commissionsearned
Recognizing UTI Symptoms in the Elderly
Recognizing UTI Symptoms in elderly can be crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Common UTI symptoms in older people include frequent urination, urgency, and a sudden change in behavior.
Physical symptoms may manifest as pain or a burning sensation during urination, blood in urine, or cloudy urine. However, it’s important to
note that UTIs in the elderly can sometimes present with atypical symptoms, making diagnosis challenging.
Caregivers should remain vigilant and aware of these typical UTI symptoms, as early detection is key.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults can include pain or a burning sensation during urination, blood in urine, cloudy urine, an unusual odor of urine. Other symptoms may include lower abdominal pain or discomfort, frequent urination, urgency, the inability to urinate in small amounts, fever, chills, or a general feeling of fatigue. These symptoms may indicate the presence of a UTI in elderly individuals.

Behavioral Changes and Their Causes
Behavioral changes like agitation, confusion, and delirium are common in older people with UTIs. These symptoms can be caused by the infection’s impact on the central nervous system.
Dehydration, a risk factor for UTIs in the elderly, can also contribute to behavioral changes. In those with dementia, a UTI can worsen symptoms and lead to sudden behavior changes.
Caregivers should be vigilant in monitoring these changes as they may be signs of an underlying UTI.

Distinguishing Between UTI and Dementia
While there are similarities in symptoms, medical professionals can differentiate between a urinary tract infection and dementia through a thorough evaluation.
UTIs in the elderly can sometimes be mistaken for symptoms of dementia, leading to a delayed or incorrect diagnosis. Importance of a correct diagnosis is crucial in providing the appropriate treatment for the elderly, whether it is a UTI, dementia, or both.
Treating a urinary tract infection in an elderly person with dementia can alleviate symptoms that may be mistakenly attributed to the progression of dementia.
Caregivers should communicate any concerns regarding the elderly person’s health to healthcare providers to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Similarities and Differences in Symptoms
Both urinary tract infections (UTIs) and dementia in older people can exhibit similar symptoms, including confusion, agitation, and changes in behavior.

However, UTIs often present with physical symptoms like pain during urination, blood in urine, or frequent urination, which are not commonly seen in dementia. It is important to note that dementia is a progressive neurological condition, while UTIs are treatable infections of the urinary system.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in differentiating between the symptoms of UTIs and dementia to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Importance of Correct Diagnosis
Correct diagnosis of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in older people is crucial for providing appropriate treatment. Misdiagnosing a UTI, especially in those with dementia, can result in unnecessary interventions and complications.
Accurate diagnosis ensures effective antibiotic treatment, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance. Prompt treatment of UTI symptoms in elderly can prevent severe complications like kidney or blood infections. Caregivers should communicate symptoms and medical history to aid in accurate diagnosis.
Risks and Complications of UTIs in Seniors
Seniors are at an increased risk of complications from urinary tract infections (UTIs), including kidney infections or sepsis.
Untreated UTIs in older adults can lead to severe symptoms, hospitalization, or the progression of underlying health conditions. Those with an enlarged prostate or urinary catheters are particularly susceptible to complications.
Prompt medical attention and treatment are necessary to prevent the progression of UTIs and the development of complications. Caregivers of older adults should be aware of the potential risks and complications and seek medical help if symptoms are present.
Risk Factors Among the Elderly
Advanced age is a well-known risk factor among older people for developing urinary tract infections. In elderly women, the combination of a short urethra and hormonal changes during menopause increases their susceptibility.
On the other hand, older men with an enlarged prostate gland may experience obstructed urine flow, leading to an increased risk of UTIs. Additionally, underlying health conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, or bladder dysfunction contribute to the vulnerability.
The use of urinary catheters, commonly employed in older adults, significantly raises the risk of urinary tract infections.
Possible Complications if Left Untreated
Delays in treating UTIs in older people can lead to severe complications. If left untreated, UTI symptoms in elderly can progress to kidney infections, potentially causing delirium or sepsis. However, prompt treatment can prevent these complications and avoid the need for hospitalization.
Recognizing the importance of timely intervention is crucial in preventing future infections and minimizing the risks associated with untreated UTIs.
Diagnosis and Treatment of UTI in Elderly
Accurately diagnosing UTIs in older people involves analyzing a urine sample, while treatment usually includes antibiotics. Healthcare providers may conduct a urine culture to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. In severe cases, intravenous antibiotics may be administered.

Timely diagnosis and treatment of UTIs are essential to prevent complications such as blood infections. Remember, proactive management of UTIs can minimize the risk of future infections.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnostic procedures play a crucial role in identifying UTIs in older people. Urinalysis is a common method used to diagnose UTIs in the elderly, helping healthcare providers detect the presence of bacteria or other abnormalities in the urine.
In some cases, a urine culture may be performed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. Additionally, diagnostic procedures take into account UTI symptoms in elderly, urinalysis results, and medical history to ensure accurate diagnosis and determine the most effective treatment.
For a comprehensive assessment, additional tests like blood tests may be required to evaluate kidney function. These procedures aid in providing proper care and preventing future infections.
Commonly Used Treatments and Their Effects
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat UTIs in older people, one of the most common infections they experience. This treatment helps reduce symptoms and prevent the infection from spreading. A course of oral antibiotics is often prescribed for elderly individuals with UTIs.
It is important to administer proper antibiotic treatment to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance and future infections. By using antibiotics promptly, caregivers can help their loved ones recover quickly from UTIs.
Preventive Measures for UTIs in Elderly
Adequate hydration is crucial in preventing UTIs in older people. Encourage regular urination and complete bladder emptying to minimize the risk. Good hygiene practices, including proper genital care, help reduce the chances of infection.
Vaginal estrogen may be beneficial for postmenopausal women in preventing future UTIs. When possible, avoid the use of urinary catheters to lower the risk of UTIs. By implementing these preventive measures, caregivers can significantly reduce the likelihood of UTIs in their loved ones.
How Can Caregivers Reduce the Risk of UTIs in Their Loved Ones?
Caregivers play a crucial role in reducing the risk of UTIs in their elderly loved ones. Encouraging adequate hydration, addressing urinary symptoms promptly, promoting good personal hygiene, monitoring for signs of infection, and being knowledgeable about risk factors and symptoms are all important preventive measures.
Once more, fortify relief for elderly UTIs with our exclusive Cranberry Blend, infused with 900 mg of Cranberry fruit essence and immune-revitalizing Vitamin C. Tackle urinary tract discomfort effectively while actively promoting holistic well-being. Elevate their health journey with our exceptional formula! #ads #commissionsearned
The Lowdown on Untreated UTIs in Our Loved Ones:
Imagine this: Your dear grandma or grandpa might be brushing off those tricky UTI symptoms, thinking it’s a passing discomfort. However, it’s essential to know that if left unattended, things can get complicated, leading to:
- Kidney Concerns (Pyelonephritis): The UTI may take an unexpected turn towards the kidneys, potentially causing lasting kidney issues.
- Sepsis Worries: While rare, an untreated UTI can escalate into sepsis, a severe condition that can be life-threatening and affect multiple organs.
- Cognitive Challenges: Unchecked UTIs might bring about sudden changes in mental clarity, like confusion or forgetfulness, affecting our loved one’s daily life.
- Recurring Issues: Chronic UTIs could become a recurring problem, making each episode more challenging to manage.
When Urgency Calls: Signs It’s Time for Professional Help
When should you consider reaching out for immediate medical assistance? Keep an eye out for these signals:
- Fever on the Rise: If their temperature rises above 101°F (38.3°C) and stays high, it’s a cue to consult healthcare professionals.
- Persistent Pain: Unrelenting pain in the abdomen or back, especially if it suggests a potential kidney infection, warrants prompt attention.
- Mental Changes: Sudden shifts in mental well-being, like confusion or unusual behavior, should be addressed promptly.
- Breathing Difficulties: If breathing becomes a struggle, seeking medical help is crucial for their well-being.
- Continuous Vomiting: Persistent vomiting, making it challenging to stay hydrated, is a concerning sign that demands urgent care.
- Lack of Improvement: If there’s no improvement within 48 hours of starting antibiotic treatment, consulting healthcare professionals is advised.
Remember, your instincts matter. If something feels off, it’s okay to seek guidance. Our seniors deserve the best care.
Reducing Risks When Caring for Elderly Loved Ones
Caregivers play a crucial role in recognizing and addressing UTI symptoms in elderly. Being aware of the physical symptoms and behavioral changes can help in early detection and prompt treatment.
It is also important to distinguish between UTI symptoms and those associated with dementia, as a proper diagnosis is essential for appropriate care. Understanding the risks and complications of UTIs in seniors emphasizes the need for preventive measures.
Caregivers can reduce the risk of UTIs by promoting good hygiene, encouraging regular bathroom breaks, and ensuring proper hydration. By being proactive and vigilant, caregivers can help maintain the health and well-being of their loved ones.
FAQs
What are the common signs and symptoms of a UTI in elderly individuals?
Common signs and symptoms of a UTI in elderly individuals include frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, confusion or behavioral changes, fever, chills, and abdominal pain. Seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a UTI in an elderly person under your care.
How can UTIs be prevented in elderly individuals?
Encourage proper hydration by ensuring elderly individuals drink plenty of water. Promote good hygiene practices, including regular bathing and wiping from front to back. Provide easy access to a restroom and encourage complete bladder emptying. Consider probiotics or cranberry supplements, but consult a healthcare professional first.
What are the potential complications of an untreated UTI in elderly individuals?
Untreated UTIs in the elderly can lead to serious complications, including sepsis, kidney damage, and delirium. Monitoring for symptoms like confusion, fever, and worsening urinary symptoms is crucial. Prompt antibiotic treatment is necessary to prevent these complications. Recurrent UTIs may benefit from preventative measures like increased hydration and regular urination.
When should a caregiver seek medical attention for their elderly loved one with UTI symptoms?
If your elderly loved one is experiencing severe symptoms like high fever, vomiting, or confusion, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. If the symptoms persist for more than 24-48 hours despite home remedies, over-the-counter medication, or if there’s a history of kidney problems or other health issues, it’s best to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional.
Stay Connected with Senior Parents!
Join our community for heartfelt guidance in senior caregiving. Follow us on social media for inspiring stories, professional tips, and invaluable wisdom today!
? Website: Explore sr-parents.com for in-depth articles and resources about senior care, health, and well-being.
? Pinterest: Discover a wealth of caregiving ideas, home hacks, and senior-friendly activities at pinterest.com/seniorparents.
? Facebook: Join our supportive community at facebook.com/sr.parents. Engage with fellow caregivers, share experiences, and find inspiration.
? Twitter: Connect with us at twitter.com/senior_parents for real-time updates, news, and trending topics related to senior care.
? Instagram: Follow us on instagram.com/seniorparents for uplifting moments, caregiving tips, and a glimpse into the lives of seniors and their families.
Follow us now and let’s start this rewarding journey together!